TOP 10:
| Product code D00153 | Currently out of stock |
"Geska 1" - phototherapy apparatus - your home doctor.
Currently out of stock
Numerous scientific studies show that sunlight can stimulate the synthesis of vitamin D in the human body and the secretion of many important biologically active substances and hormones. Sunlight can affect the function of the cardiovascular and immune systems, as well as the brain. Finally, it is sunlight that determines the biological rhythms of our body. Scientists seriously consider living north of 40 degrees north latitude and south of 40 degrees south latitude (i.e., in areas where there is a deficit of sunlight in winter) as one of the important risk factors for many diseases.
By the early 1990s, new LEDs were created, a new element base, combining portability and very high power, on the basis of which very compact devices for the so-called home phototherapy were created. And one of these devices was the Geska apparatus. The uniqueness of the device is that it compensates for the lack of light, just what a person usually does not notice.
Geska is a source of powerful radiation (monochromatic red and infrared), which in its parameters is close to laser. This was achieved thanks to a unique technology, which for the first time made it possible to create a portable device that has most of the functions of complex and expensive laser therapy devices. However, at the same time "Geska" compares favorably with such indicators as safety, compactness and ease of use.
Diseases in the treatment of which Geska really helps:
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system:
Treatment of arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, infectious - allergic arthritis
Nervous system pathologies
Treatment of osteochondrosis and osteoarthritis of the spine
Facial nerve neuritis
Trinity neuralgia
Vegetovascular and neurocirculatory dystonia
Diseases of the bronchopulmonary system
Acute respiratory infections (ARI), tracheitis, bronchitis
Acute pneumonia, bronchial asthma
Prevention of influenza, acute respiratory diseases (ARI) and protection of the body during the transition from winter to summer and from summer to winter
Surgical pathologies
Acute purulent diseases - boils, infiltrates, carbuncles, purulent ulcers, skin burns, phlegmon, pustular eruptions
Trophic ulcers
Long-term non-healing wounds or wounds that heal by secondary intention, bone fractures
Phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, varicose veins
Sprains, subluxations of joints
Skin diseases
Atopic dermatitis, eczema, psoriatic arthritis, scleroderma
Psoriasis
Herpetic skin diseases
Diseases of the ear, throat, nose
Otitis media, ethmoiditis
Rhinitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis (acute and chronic)
Tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis
Cardiovascular diseases
Hypertonic disease
Ischemic heart disease, exertional angina
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Gastritis, peptic ulcer, cholecystitis, pancreatitis
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Treatment of arthrosis, rheumatoid arthritis, infectious-allergic arthritis
Supravenous blood irradiation (elbow and axillary folds for the upper extremities, inguinal and popliteal folds for the lower extremities). The exposure time is from 5 to 10 minutes for each field, the number of procedures is from 3 to 5 per course of treatment, for rheumatoid arthritis - up to 10 procedures. The radiation fields of the affected joints are shown in Fig. 2.
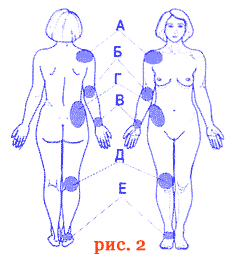
Field exposure: A - shoulder joint, B - the elbow, in the - wrist joint, T - hip, E - knee, E - the ankle joint.
The exposure time is from 10 to 20 minutes per joint, the number of procedures is from 2 to 10. Procedures can be performed from one to 2 to 3 times a day, with a total duration of the procedure up to one hour for adults, up to 30 minutes for children over 3 years old and up to 20 minutes - under 3 years old. In case of rheumatoid, infectious-allergic, psoriatic, rheumatic polyarthritis, supravenous blood irradiation is recommended; in case of monoarthritis, it is sufficient to irradiate only the joint area.
Nervous system pathologies.
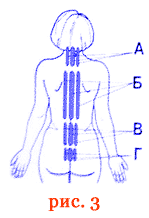
Treatment of osteochondrosis and osteoarthritis of the spine
Skin exposure along the fields along the spine in the center and symmetrically (paravertebral) to the left and right of the center. Emphasis is placed on the spine (Figure 3.) Neck - A , thoracic - B , lumbar - V sacrum - G , where localized aggravation.
The duration of exposure is from 20 to 30 minutes, 1 - 3 times a day until the pain stops and the mobility of the spine is restored (up to 10 - 15 sessions).
Neuritis of the facial nerve
Cutaneous action along the fields in the area of the exit from the skull of the trunk of the facial nerve and along the projection of its branches. The irradiation fields are shown in Fig. 4: field A - with damage to the 1st branch of the facial nerve; field B - in case of damage to the 2nd branch of the facial nerve; field B - with damage to the 3rd branch of the facial nerve. At any location of the lesion of the facial nerve necessarily impact on the field D .
The total exposure time for one procedure is up to 10 - 12 minutes, 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 8 - 12 procedures.

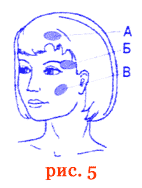
Neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve
Cutaneous action along the fields in the area of the exit from the skull of the branches of the trigeminal nerve. The irradiation fields are shown in Fig. 5. A - with damage to the first branch of the trigeminal nerve; B - with damage to the second branch of the trigeminal nerve; B - with damage to the third branch of the trigeminal nerve.
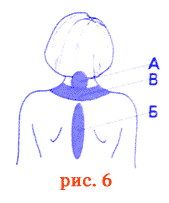
Vegetovascular and neurocirculatory dystonia
Supravenous blood irradiation (elbow bend, popliteal fold) - from 5 to 10 minutes per field, number of procedures - 3 - 4. Skin irradiation in the corresponding fields. The fields of influence are shown in Fig. 6. Irradiation of the cervical spine A - 1 min. on the field, the irradiation of the thoracic spine B and neck area in - 10 minutes, the number of procedures 5 - 8.
Diseases of the bronchopulmonary system
Acute respiratory infections, tracheitis, bronchitis
Supravenous and supra-arterial blood irradiation in the area of the armpits, elbows 5 - 10 min.
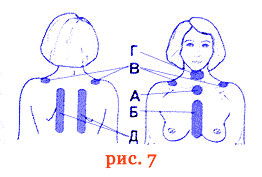
Skin irradiation in the corresponding fields (Fig. 7): A - area of the jugular fossa; B - the middle line of the sternum; B - shoulder girdle area; G - submandibular region; D - the spine is paravertebral to the right and left. Irradiation time 3 - 5 minutes on the field.
The procedures are carried out 1 - 2 times a day until recovery. It is possible to combine and carry out in one day procedures for skin exposure, supravenous and supra-arterial blood irradiation.
Acute pneumonia, bronchial asthma
Supravenous and supra-arterial blood irradiation in the area of armpits, elbows (Fig. 8) for 5 - 10 minutes on the field.
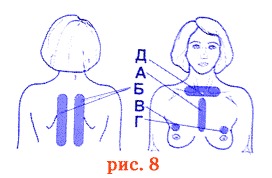
But cutaneous exposure fields: the middle line of the sternum And , paravertebrally field thoracic spine left and right B , the affected area corresponding to the lobe of the lung ( in at right-sided pneumonia), bronchi roots of D 10 - 15 minutes on the field.
In case of left-sided pneumonia, instead of point B, irradiate the symmetrical point G on the left. The number of procedures is 8 - 10.
Prevention of influenza, acute respiratory diseases and protection of the body during the transition from winter to summer, and from summer to winter
At the end of winter, in spring and even at the beginning of summer, a weakened body is at risk of colds and requires very careful attention and, if possible, preventive protection. Particular attention must be paid to preventive protection against influenza epidemics. Prevention of colds (acute respiratory) diseases and influenza is carried out by the device's radiation exposure to the area of the maxillary and frontal sinuses (zone A), the upper part of the sternum (zone C), as well as the collar zone (zone B) (Fig. 9).
The duration of the prophylaxis course is 3 - 5 days, once a day in the morning or in the evening.
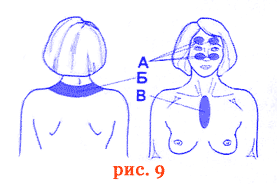
Flu prophylaxis is advisable to carry out 2 - 3 weeks before the onset of the epidemiological situation.
Surgical pathologies
Good results are obtained by the use of radiation in operating surgery due to preoperative treatment of the operating field 30-40 minutes before the operation for 15-20 minutes, followed by intensive irradiation of the operation area 3-4 hours after its completion 3-4 times a day ... The overgrowth of the seam occurs 30-40% of the time faster and the size of the keloid scar is significantly reduced.
Acute purulent diseases - boils, infiltrates, carbuncles, purulent ulcers, skin burns, phlegmon, pustular eruptions
Treatment of small localized purulent pathologies and burns is carried out in the area of the lesion for 20 - 30 minutes with the capture of the surrounding healthy skin 2 - 3 times a day, for 2 - 3 days until cure. In the treatment of boils, carbuncles, extensive purulent ulcers and phlegmon (after their surgical opening), the overlying vascular zones (axillary, elbow, inguinal or popliteal areas) are irradiated for 5-10 minutes per zone, and then the zone of the purulent focus is irradiated from 15 to 30 min 2 - 3 times a day until recovery.
Trophic ulcers
Treatment should be started with supravenous blood irradiation. If the ulcer is located on the lower extremities, then the inguinal and popliteal folds on the left and right are irradiated; if the ulcer is located on the upper extremities, the axillary and elbow folds on the right and left are irradiated for 5-10 minutes per area, only 5-7 days. Then, the entire affected skin surface is irradiated with the capture of healthy tissues within 2 - 3 cm, moving from the periphery to the center of the pathological area.
The exposure time is from 15 to 20 minutes, 2 to 3 times a day until scarring. To these areas, you can reduce the radiation for 10 minutes in the sternum area in order to further stimulate the immune system.
Long-term non-healing wounds or wounds that heal by secondary intention, bone fractures
Irradiation of the sternum 10 - 15 minutes and the lesion site from 20 to 40 minutes 2 - 3 times a day, a total of 6 - 8 days. Irradiation is carried out in the fields, capturing the entire wound surface and healthy tissues within 1 - 1.5 cm and moving from the periphery to the center of the wound. In case of fractures of tubular bones, irradiation is carried out in one field from opposite sides in the fracture area towards each other, in case of a fracture of flat bones (ribs, sternum, clavicle) - one field in the fracture area.
Phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, varicose veins
In case of phlebitis, thrombophlebitis, irradiation is carried out along the projections of the affected vein from the periphery to the center (from bottom to top) in successive fields overlapping each other. The impact on the affected limb can be started after normalization of the local temperature, reduction of pain, the exposure time is from 15 to 30 minutes. In the presence of varicose veins - an additional effect on them. The total number of procedures up to 10 - 12
Sprains, subluxations of the joints
The exposure is carried out locally at the site of injury, contactlessly or by contact for 20 - 40 minutes 2 - 3 times a day.
Skin diseases
Basic therapy: irradiation of the sternum and spine for 10 - 15 minutes on the field and skin lesions. Irradiation is carried out along the fields of pathology, capturing the entire affected surface of the skin from the periphery to the center with mandatory irradiation of healthy tissues within 1 - 1.5 cm from the border of the affected area.
Atonic dermatitis, eczema, psoriatic arthritis, scleroderma
In the treatment of these diseases, the exposure time on the lesions is 10-15 minutes twice a day. The duration of the course is 10 - 15 days.
Psoriasis
With a significant spread of psoriasis skin lesions, the treatment process is recommended to be carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist. With limited lesions of the skin with psoriasis, phototherapy is carried out for 20 - 25 minutes on the focus, twice a day for 13 - 15 days.
Herpetic skin diseases
In limited areas of the lesion, the exposure time to the affected area is 10 minutes. With a large spread of lesions, the irradiation is carried out for 15 - 20 minutes by sequential movement of the device over the entire surface of the affected area. In both cases, radiation is performed once a day. The course of treatment is 3 - 5 procedures.
Herpes simplex: only the area of the rash is irradiated from 10 to 15 minutes, 4 to 5 or more times a day. The duration of treatment is 1 - 2 days. The greatest effect of exposure is obtained when the corresponding area of the skin is irradiated at an early stage of the onset of skin manifestations, in the presence of only itching or burning and the absence of other elements of the herpetic process.
Diseases of the ear, throat, nose
Otitis media, ethmoiditis
Local irradiation of the near- and behind-the-ear region, as well as the external auditory canal for 10 minutes in the field 3 - 4 times a day. Additionally, the sternum (E) and the submandibular region (D) are irradiated (Fig. 10) for 5-10 minutes on the field, the number of procedures is
3-4 . Rhinitis, sinusitis, frontal sinusitis (acute and chronic).
Irradiation of the nasal wing region (C ), nose (B), maxillary sinuses (A), additionally - submandibular areas (D), irradiation of the sternum (C) for 5 - 10 minutes per field, the number of procedures 3 - 4.
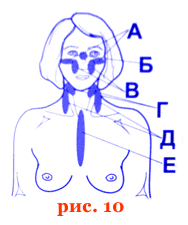
Tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis
Irradiation of the submandibular region (D) 5 minutes, the sternum (E) 10 minutes and the area of inflammation (lateral surfaces of the neck) (E) (Fig. 10) from 15 to 30 minutes 2 - 3 times a day, 2 - 3 days.
Cardiovascular diseases
Hypertension The
therapeutic effect is achieved by irradiating the reflexogenic zones of the collar region for up to 10 minutes per procedure once a day, the number of procedures
is 8-10.Fields of influence: A - paravertebral right and left, B - shoulder girdle area, C - supraclavicular the area at the level of the middle of the clavicle (Fig. 11)

Ischemic heart disease, exertional angina
Supravenous blood irradiation in the elbow bend area, cutaneous exposure along the fields: A - middle of the left sternocleidomastoid muscle: B - second intercostal space to the right of the sternum: C - second intercostal space to the left of the sternum: D - fourth intercostal space along the left mid-clavicular line (Fig. 12).
A combination of fields of influence: without cardiac arrhythmias - fields B, C, D in the presence of cardiac arrhythmias - fields A, B, C, D. The procedure is carried out until the pain syndrome is relieved (5-15 minutes).
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract
Gastritis, peptic ulcer, cholecystitis, pancreatitis
Paravertebral irradiation of the spine (Fig. 13) - 10 - 15 minutes, local irradiation of the projection of the affected organ for 15 - 25 minutes, for a course of treatment 6 - 8 sessions.
Similar products
Copyright © 2001- All rights reserved Lerson.ee